BASIC ELEMENTS OF COMPUTER
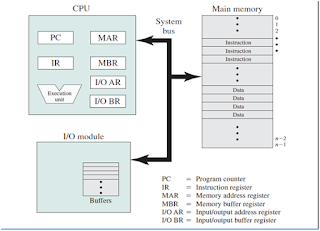
A computer consists of the processor, memory, and I/O components, with one or more modules of each type. These components are interconnected in some fashion to achieve the main function of the computer, which is to execute programs. Thus, there are four main structural elements:
1. Processor: Controls the operation of the computer and performs its data processing functions. When there is only one processor, it is often referred to as the central processing unit (CPU).
2. Main memory: Stores data and programs. This memory is typically volatile; that is when the computer is shutdown, the contents of the memory are lost. In contrast, the contents of disk memory are retained even when the computer system is shut down. Main memory is also referred to as real memory or primary memory.
3. I/O modules: Move data between the computer and its external environment. The external environment consists of a variety of devices, including secondary memory devices (e.g., disks), communications equipment, and terminals. An I/O module transfers data from external devices to processor and memory, and vice versa. It contains internal buffers for temporarily holding data until they can be sent on.
4. System bus: Provides for communication among processors, main memory, and I/O modules.
The figure depicts these top-level components. One of the processor’s functions is to exchange data with memory. For this purpose, it typically makes use of two internal (to the processor) registers: MAR And MBR
MAR: Memory addresses register (MAR), which specifies the address in memory for the next read or write.
MBR memory buffer register (MBR): This contains the data to be written into memory or which receives the data read from memory.
I/O addresses register (I/OAR) specifies a particular I/O device.
An I/O buffer register (I/OBR) is used for the exchange of data between an I/O module and the processor.

Comments
Post a Comment